Acupuncture for Inflammation
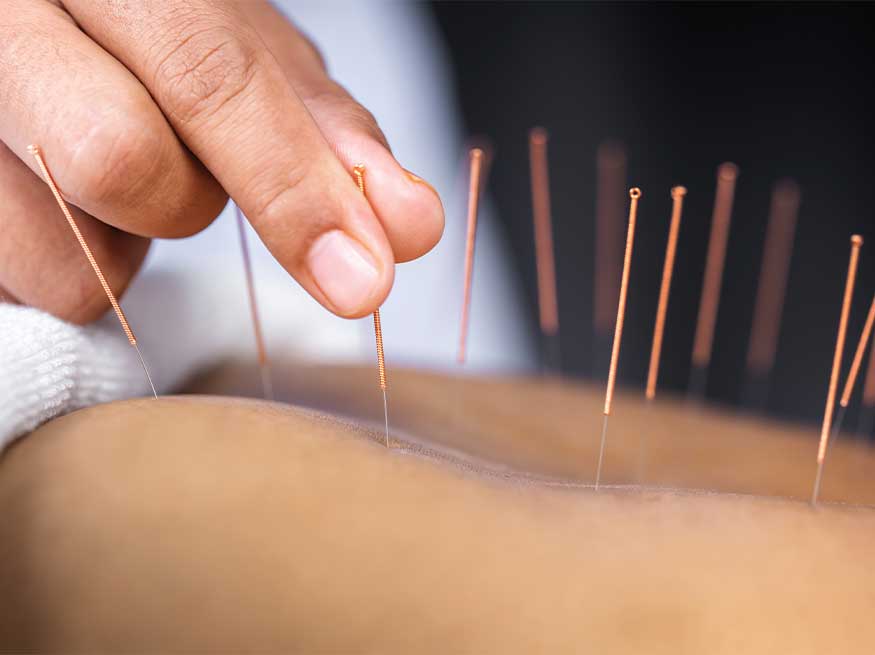
Acupuncture, an ancient technique originating from traditional Chinese medicine, has been increasingly explored as a potential treatment for inflammatory conditions.
By targeting specific acupuncture points that correspond with hypersensitive spots in the body, this practice may offer therapeutic benefits by modulating the immune response and promoting physiological balance.
Clinical studies investigating the efficacy of acupuncture in inflammation management will be discussed, along with potential mechanisms underlying its anti-inflammatory effects.
What is Acupuncture?
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body to promote therapeutic effects. It is based on the concept of Qi, an energy force believed to flow through pathways called meridians in the body. According to traditional Chinese medicine, disruptions or imbalances in this flow can lead to various health problems.
The exact mechanisms by which acupuncture works are not fully understood, but several theories have been proposed. One theory suggests that acupuncture stimulates nerve fibers, leading to the release of endorphins and other neurotransmitters that help alleviate pain and promote relaxation. Another theory proposes that acupuncture may modulate immune responses by influencing cytokines and other immune factors.
Research on acupuncture has shown mixed results, with some studies suggesting its effectiveness for certain conditions while others find no significant benefits beyond placebo effects. However, meta-analyses have indicated potential positive effects of acupuncture for chronic pain conditions such as back pain, osteoarthritis, and migraines.
It is important to note that while acupuncture is generally considered safe when performed by trained practitioners using sterile needles, there are risks associated with improper technique or unsterilized equipment. Therefore, it is recommended to seek treatment from licensed acupuncturists who follow proper safety protocols.
Inflammatory Conditions
Immunomodulatory therapies have been explored as potential treatments for various inflammatory conditions. Inflammation is a natural response of the immune system to protect the body from harmful stimuli, such as pathogens or tissue damage. However, excessive or chronic inflammation can lead to various diseases and conditions. Traditional treatment options for these conditions often involve anti-inflammatory medications; however, immunomodulatory therapies aim to modulate the immune response more specifically.
These therapies may include biological agents targeting specific molecules involved in inflammation or immunosuppressive drugs that dampen overall immune activity. By targeting specific components of the immune response involved in inflammation, immunomodulatory therapies hold promise for more targeted and effective treatment options for patients with inflammatory conditions. Further research is needed to fully understand their benefits and potential side effects.
Here are five common inflammatory conditions:
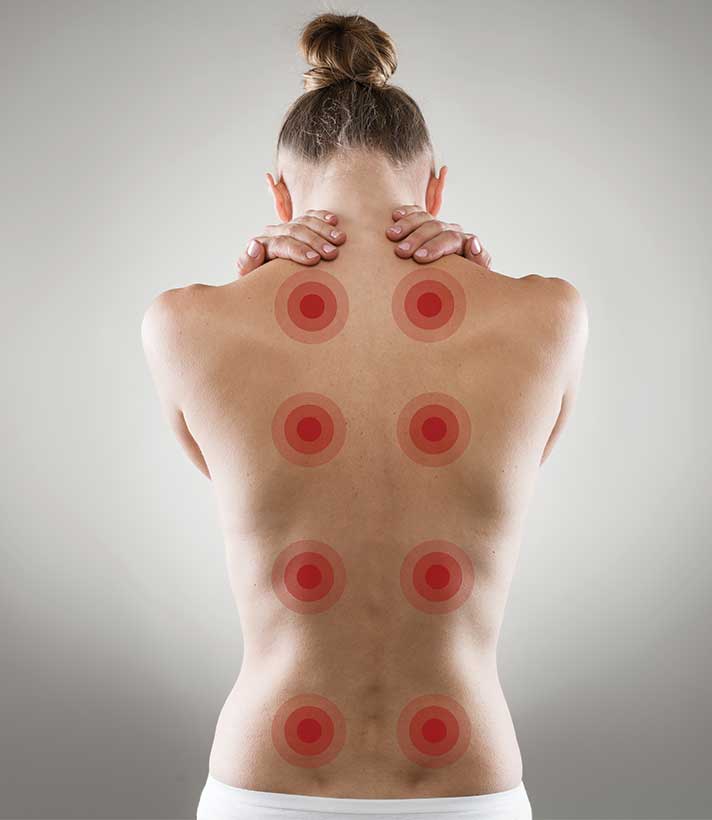
Acupuncture Points and Hypersensitive Spots
The identification and stimulation of specific points on the body, known as acupuncture points, have been found to be associated with hypersensitive spots that may play a role in the treatment of various conditions. Acupuncture points are believed to be areas where there is increased electrical conductivity compared to surrounding tissues. These points have been mapped out and identified over centuries by traditional Chinese medicine practitioners. They are located along channels or meridians that are thought to carry energy or Qi throughout the body.
Hypersensitive spots, also known as trigger points, refer to localized areas of tenderness or discomfort that can be found in muscles, fascia, or connective tissues. These spots can be sensitive to palpation and often correspond with specific acupuncture points. The relationship between acupuncture points and hypersensitive spots has led researchers to hypothesize that these spots may represent areas of altered tissue function or dysfunction.
Studies have shown that acupuncture stimulation at these hypersensitive spots can lead to physiological responses such as increased blood flow, release of endorphins, and modulation of the autonomic nervous system. This suggests that stimulating these points through acupuncture may help regulate various physiological processes involved in inflammation and pain.
While further research is needed to fully understand the mechanisms underlying the effects of acupuncture on hypersensitive spots and their potential therapeutic applications for inflammation-related conditions, preliminary evidence suggests that targeting these specific points may offer a promising approach to managing inflammatory symptoms.
Ways Acupuncture Reduces Inflammation
One potential mechanism by which acupuncture may reduce inflammation is through the regulation of immune responses. Acupuncture has been shown to modulate the activity of various immune cells, such as macrophages, T cells, and natural killer cells. These immune cells play crucial roles in the inflammatory response and can either promote or suppress inflammation depending on their activation state.
There are several ways in which acupuncture affects immune responses and reduces inflammation:
Overall, these mechanisms demonstrate how acupuncture can modulate immune responses and reduce inflammation in a variety of conditions.
Acupuncture has been found to be a potentially effective treatment for inflammation. Clinical studies have shown that acupuncture can help reduce inflammation by stimulating specific points in the body that correspond with hypersensitive spots.
This ancient technique has been adapted and incorporated into modern medicine as a complementary therapy for inflammatory conditions. Additionally, research suggests that acupuncture may work through the vagus nerve to regulate the body’s immune response and decrease inflammation.
Acupuncture offers a promising alternative approach to managing inflammation in a safe and evidence-based manner.
